|
as of 6 Feb 2019 Results of my FTDNA Y-DNA37 test Kit No. 892549
- I have 16 matches to the "Eaton" surname
 31 Aug 2019 with 8) 37marker and 8) 25markers
31 Aug 2019 with 8) 37marker and 8) 25markers
Ancestry
DNA
results (online link), Per
Ancestry as of 7 Aug 2019 - Your DNA doesn’t change, but the science we
(Ancestry) use to
analyze it does. Your results may change over time as the science improves.
This test compares your DNA with I believe only those Subscribers of Ancestry
who themselves have taken the DNA Test at the time you submit.
I am Looking for Descendants of
Claude Brudenell Eaton (1879-???) of New
Hartford, Oneida Co., NY
as of 5 Feb 2019 FTDNA
confirmed my being an Eaton connecting back to Francis Eaton (1595-1633) of the
Mayflower
Update: since
my DNA posting 16 Dec 2016, I
now have over 30,000 5th-8th Cousins, several Hundred 4th-6th Cousins, several
2nd-3rd Cousins as a result of my AncestryDNA Autosomal test.
The real challenge of DNA matching is to
make sure that any identical pieces of DNA we (Ancestry) find are really
identical because of a recent shared ancestor—rather than ancient shared
history.
There are other reasons why two people’s
DNA could be identical. After all, the genomes of any two humans are 99.9
percent identical. (And the genome of a human is 50 percent identical to
the genome of a banana.) Pieces of DNA could be identical between two people
because they are both human, because they are of the same ethnicity or come from
the same region, because they share some other more ancient shared history, or
other reasons. We (Ancestry) call these identical pieces of DNA identical
by state (IBS), because the DNA is identical for a reason other than having a
recent shared common ancestor.
Looking at the DNA sequence alone
doesn’t tell us the difference, so we’ve (Ancestry) developed a ground-breaking
scientific method that helps to distinguish DNA that is IBD (Identical By
Descent) from DNA that is not. Our (Ancestry) method looks at not only the
amount of identical DNA between two people, but also its location in the genome
and other features. (Get
more details on the process in our white paper pdf) If we find that you have
identical DNA with a potential DNA match that appears to be IBS (identical by
state) and due more to an ancient shared history, we won’t show them in your
list of matches.
I feel Results are also in
Combination with Matching your online Family Tree Ancestors (from my 30+ years
of researching since 1992), with other's who have posted Private or Public
Trees, which may contain 3 to over 77,000 Ancestral Names, unknown to myself
which shared Ancestor we have in common.
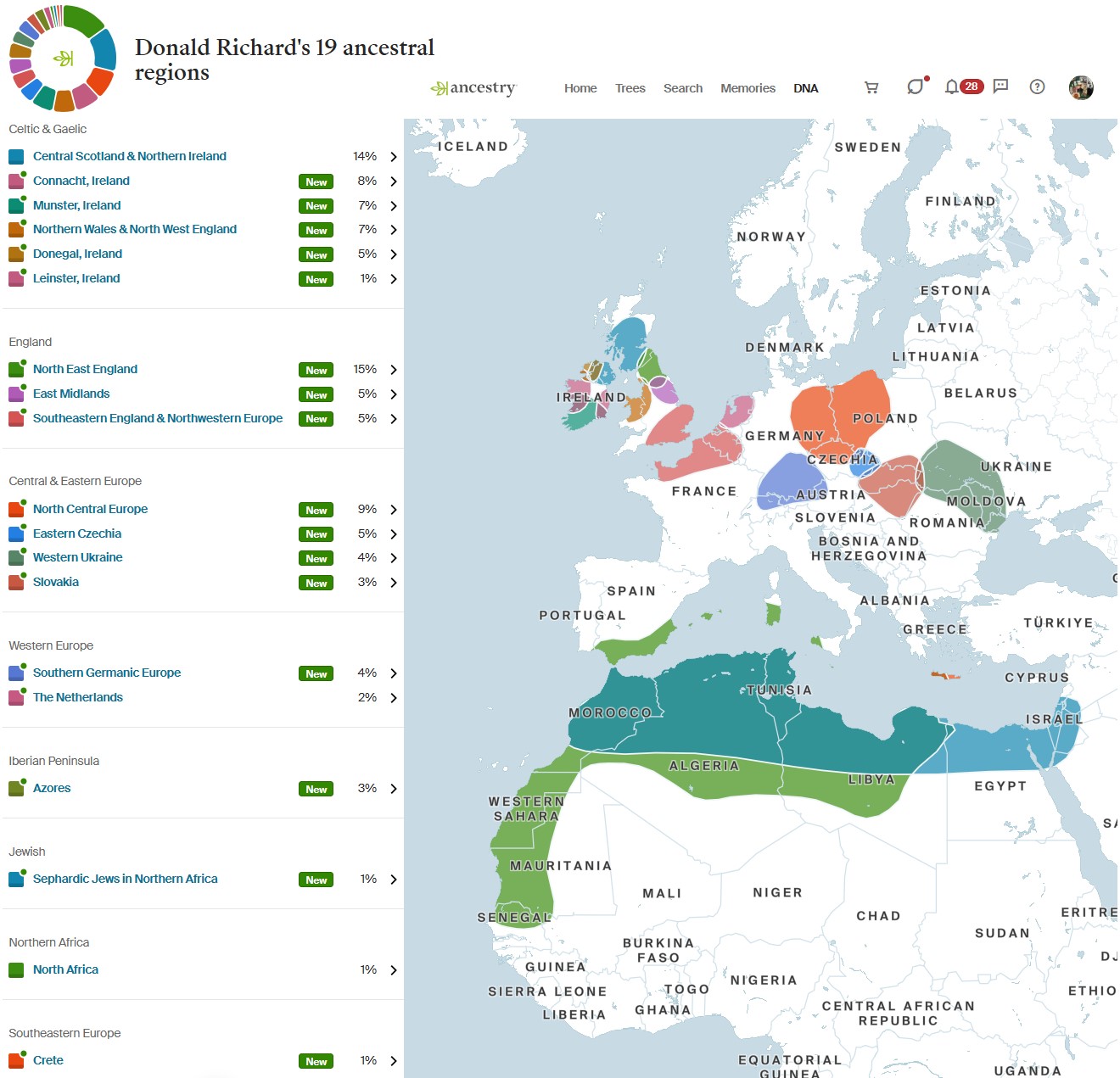
Previous DNA Estimate by Regions from 14Dec2016 - Now Compare to
Nov 2025 DNA
Estimate of 19 Regions

Watch "AncestryDNA:
Updates for 2025 Video" with more than 3,600 Places
from Around the World and 68 New Updated European Regions
Watch "AncestryDNA:
Updates for 2025 Video" with more than 3,600 Places
from Around the World and 68 New Updated European Regions
 <------ Visit
<------ Visit
Genetic Differences
In regards to yDNA, a rough outline of Genetic
Distance for each level of STR* testing can be found in following
link.*STR
(short tandem repeat) markers are regions of DNA with short,
repeating sequences that are highly variable between individuals.
These charts are base on the average rate of STR marker mutations**.
One can be higher then average or lower then average which will skew
results....
12marker
https://www.familytreedna.com/learn/...s-interpreted/
25 marker
https://www.familytreedna.com/learn/...s-interpreted/
37 marker
https://www.familytreedna.com/learn/...s-interpreted/
67 marker
https://www.familytreedna.com/learn/...s-interpreted/
111 marker
https://www.familytreedna.com/learn/...s-interpreted/
**STR
marker mutations are changes in the number of repeat units in short
tandem repeats (STRs), occurring primarily through strand slippage
during DNA replication. These mutations can lead to either a
gain or loss of repeat units and are a common source of variation,
but their frequency can vary based on the STR locus and other
factors. They are a key consideration in fields like forensic
science and paternity testing, where they can appear as non-Mendelian
inheritance patterns between parents and offspring.
The Following DNA Links is for information use, if you find information of
use/helps in understanding more about DNA. All Sites/Links I provide, I have
visited and My Norton Security nor MalwareBytes has Alerted to suspicious
content, adware, malicious, a treat virus or trojan, etc. I do not know of
Security Software that is 100% Guaranteed to Block, Prevent and Stop every
threat.
Your DNA
Guide
https://www.yourdnaguide.com/scp
Beginner's Guide
to Shared Centimorgans
https://whoareyoumadeof.com/blog/2018/02/21/beginners-guide-shared-centimorgans/
Who Are You Made of DNA Tool
Page
https://whoareyoumadeof.com/start-here/

| 



